Research Utilization and Advancing Prototypes
Research Utilization and Advancing Prototypes
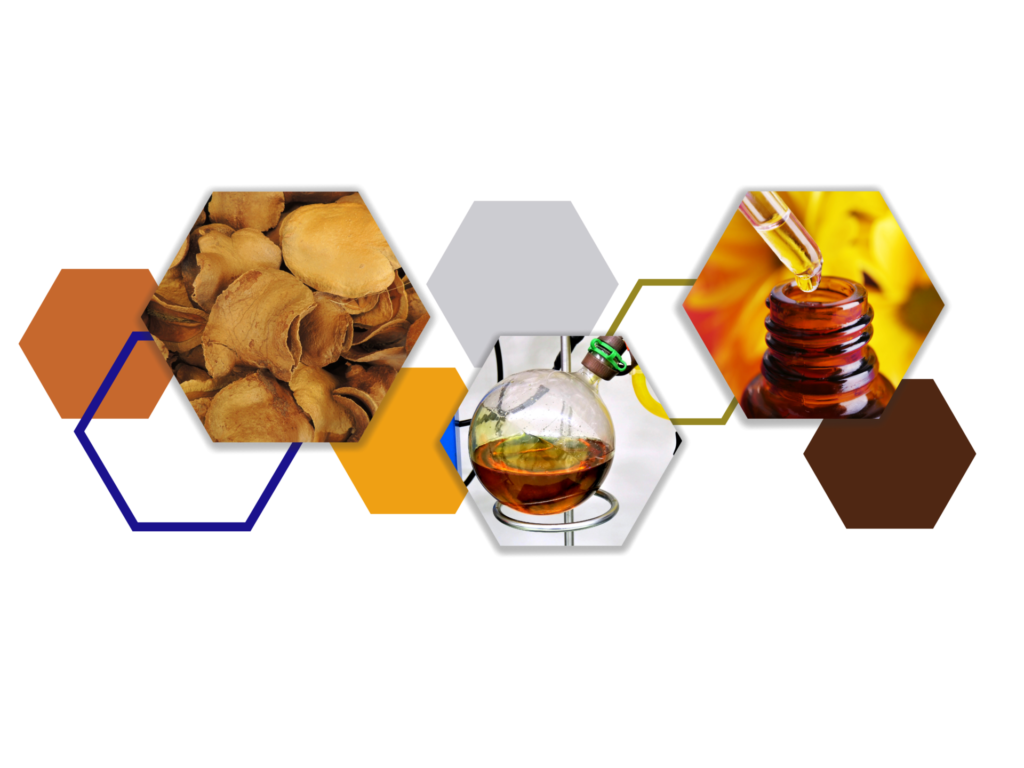



Our laboratory has emphasized on the importance of research utilization in the areas of polymer sciences for medical devices and standardized preparation of Kratom extracts as well as essential oils, with an ultimate aim for their applications in the industry. Standardized herbal extracts and essential oils such as those from mangosteen peels, galanga, betel vine, white turmeric, and white ginger have been developed on a lab/pre-pilot scale.
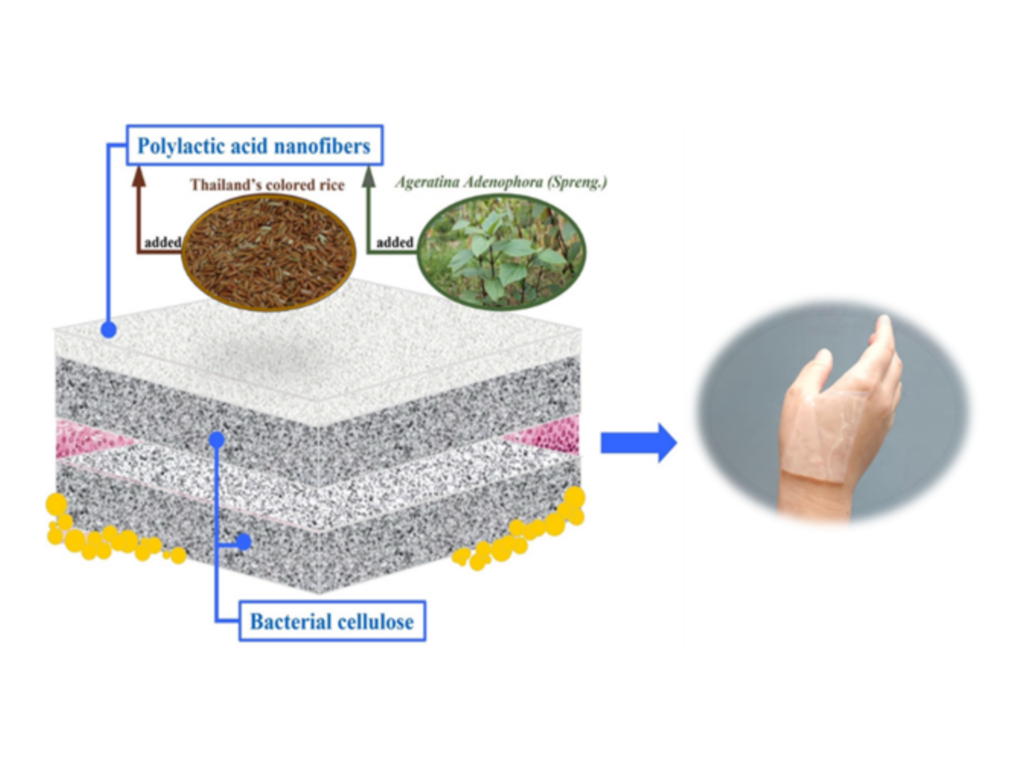
Double-layered wound dressing from biopolymer mixed with Thai herbal extracts has been formulated. The first layer of bacterial cellulose raised with coconut juice provides not only moisture during the healing process, thereby reducing irritation upon peeling it off, but also matrix to absorb exudates from the wound. The second layer consists of polylactic acid nanofiber prepared via electrospinning process; it also contains antioxidants from rice extracts and antibacterial essential oils from Crofton weed. This wound dressing also exhibits good safety profile toward human skin as both rice extracts and essential oils are non-cytotoxic against human dermal fibroblasts and human keratinocytes. The development has relied on local materials, thereby reducing the costs of imports and strengthening the local industry in wound dressing to effectively cater to the patients’ needs.
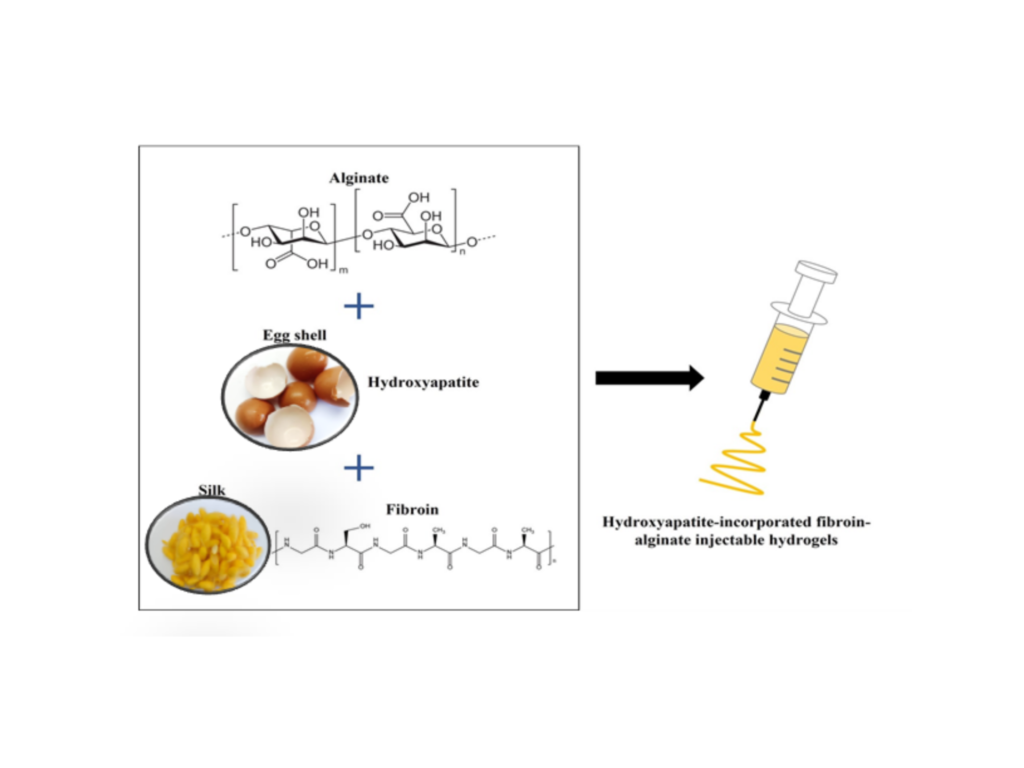
The eggshell-derived hydroxyapatite-incorporated fibroin-alginate composite injectable hydrogel has been fabricated as scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Hydroxyapatite derivable from eggshell biowaste provides calcium phosphate-based ceramic-like materials with chemical constituents and structures similar to those of the bone and tooth. Extraction of Bombyx mori cocoon biowaste also provides fibroin whose proteins are compatible with human tissues and resemble bone and dental collagens. Further studies in animal models and human are warranted to advance this polymer technology. Taken together, this corroborates well with recycling biowastes and reducing the amount of import, thus allowing patients to access this medical device more cost-effectively.





